|
|
|
Evaluation ProcessNotes to consider: The quality and resolution of the images might differ from one dataset to another. The dataset is real and illustrates what researchers might face when exploring different datasets. To submit: Send a text describing the results the participants found, along with a link to your results (GitLab or other). Participants will provide: 1. Pairwise distances from all images to all images in each subset 2. Binary label (0 = authentic, 1 = imitation) for each image in each subset, or a merged CSV file covering all three subsets with the labels “ “Pizan” or “not-Pizan”, “Tasso” or “not-Tasso”, “Yaqut” or “not-Yaqut”. 3. Documentation of the classification process, namely which script features influence the distance between images and the final classification As the task is a crisp classification task, the ranking is based on the average accuracy of the output 2. “Classification label”. With:
Standard metrics are:
The overall ranking is based on the Unweighted Average Recall (UAR), also known as Balanced Accuracy or macro-averaged recall. This metric ensures fair evaluation across subsets of different sizes by computing accuracy for each subset independently and then averaging. Let S be the total number of subsets. Then the Overall Accuracy is:
where: ● N i = number of samples in subset iii, ● ● ● 1{·} = 1 if the prediction is correct, 0 otherwise.
We will not apply asymmetric costs between false positives and false negatives. While in forensic authentication tasks, accepting a forgery (FP) is typically considered more severe than rejecting an authentic work (FN), there is no established consensus in the literature on the appropriate cost ratio for writer identification tasks. For transparency and comparability, we therefore use symmetric evaluation. All patches and images are weighted equally in the evaluation, regardless of differences in textual content length. This design choice prioritizes: - Simplicity and transparency of evaluation We acknowledge that longer texts may provide more discriminative information, but leave content-aware weighting to future iterations of the competition. Distance-Based Retrieval Metrics (Diagnostic) In addition to classification accuracy, we evaluate the quality of the learned distance metric through retrieval metrics. These metrics help diagnose whether errors stem from poor feature representations or suboptimal classification thresholds.
● Top-k Retrieval Accuracy For each image in a subset, we rank all other images by their distance (ascending order) and check if images of the same class appear in the top-k nearest neighbors. Top-k Accuracy is defined as: where: - N = total number of images in the subset We report Top-1, Top-3, and Top-5 Accuracy, averaged across all subsets:
Although the task is one of crisp classification, the measure of top-k accuracy will complement the observation on accuracy if the distance metric is good, but the classification threshold needs tuning.
Ranking Impact These metrics are NOT used for the primary ranking but will be: |

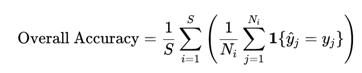
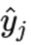 y^ j = predicted label for sample j in subset i,
y^ j = predicted label for sample j in subset i,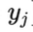 y j = true label,
y j = true label,